-
Roadkill Segway (pk) 22:240:00/22:24
-
Good ol tunes Mix 15:300:00/15:30
-
Last Chance Band - Mix 11:000:00/11:00
-
Pocket Hamsters 10:200:00/10:20
Human Influence on the Weather

The Worlds Weather and the Human Factor
To understand how human caused global warming can make winter storms more severe in some areas while other areas hardly experience winter at all, one should first take a look at two major governors of Northern Hemisphere weather: the circumpolar Jet Stream and Arctic sea ice.
An extreme difference between the temperatures at high northern latitudes and at more temperate latitudes has driven a very rapid flow of upper level air called the Jet Stream for almost all of human meteorological reckoning. This high temperature difference drove powerful upper level winds from west to east. These winds tended to modulate only slightly and when they did, powerful weather events tended to occur.
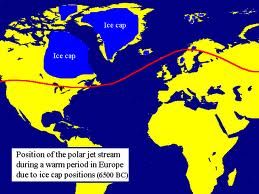
Locking a greater portion of this cold air in place was the northern hemisphere ice cap, most of which was composed of a large swath of sea ice covering much of the northern oceans. This high volume of cold, reflective ice kept temperatures up north very, very low and provided the massive temperature differences which kept the Jet Stream predominantly flat with only occasional and more moderate severe weather causing ripples and bulges.
But since 1979, massive volumes of sea ice have been lost due to an immense and ongoing human caused warming trend taking hold in the Arctic. As human greenhouse gas emissions sky-rocketed, Arctic temperatures rapidly increased far faster than the global average. By this year, human greenhouse gas emissions had driven CO2 levels to the highest seen in more than 3 million years while Arctic temperatures are now warmer than at any time in the past 150,000 years. Sea ice retreat has been equally unprecedented with average winter values now 15-20% below extent measures seen during 1979 and with end summer sea ice extent values now a stunning 35-50% below that of 1979. Sea ice volume, the measure of total ice including its thickness, has shown even more stunning losses since 1979 with seasonal winter values 30-35% lower than in 1979 and end summer values between 65 and 80% lower during recent years.
The loss of hundreds of thousands of square kilometers of sea ice radically reduces the Arctic Ocean’s ability to keep the Arctic cold. To the contrary, we see larger areas of open water that, in turn, radiate ocean heat into the atmosphere throughout winter. As a result the temperature difference between the Arctic and temperate regions is less and this, in turn, slows down the Jet Stream.
When the Jet Stream slows, it tends to meander. And when it meanders it creates very deep troughs and very large ridges. In the ridges, we get unseasonably hot temperatures along with increased risk of drought. And in the troughs, Arctic air swoops down to collide with warmer, moist air in a series of powerful storms. During the summer time, the hot, dry zones can bring deadly heat waves, record droughts, and major wildfires while the cooler stormier zones can bring epic rainfall events or even link up with tropical cyclones to result in highly severe hybrid storms. During the winter time, the hot zones can almost completely obliterate the winter season, while the stormy cooler zones can result in snow storm after snow storm.
Global temperature maps also show anomalously warm temperature departures for much of the Arctic as well as for regions beneath these powerful jet stream ridges. Note that the only northern hemisphere region showing strong anomalously cool conditions is a large swath adjacent to the large trough over North America and southern Greenland.
Temperature averages in the Arctic region of Kamchatka, the Bering Sea, the Chukchi Sea and Alaska have ranged between 11- and 12 degrees Celsius above average for the first week of December with much of the Arctic showing 4-12 degrees Celsius above average readings.
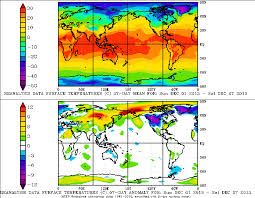 The US and southern Canada, conversely, have shown temperatures 4-10 degress Celsius below average. It is also worth noting the massive swath of 3-12 C above average temperatures stretching all the way from the Middle East to the west coast of Greenland. Thanks to Robertscribbler
The US and southern Canada, conversely, have shown temperatures 4-10 degress Celsius below average. It is also worth noting the massive swath of 3-12 C above average temperatures stretching all the way from the Middle East to the west coast of Greenland. Thanks to RobertscribblerCloud's
The Jet Stream
Weird Weather
Is Weird Winter Weather Related to Climate Change?
Scientists are trying to understand if the unusual weather in the Northern Hemisphere this winter — from record heat in Alaska to unprecedented flooding in Britain — is linked to climate change. One thing seems clear: Shifts in the jet stream play a key role and could become even more disruptive as the world warms. Fred Pearce
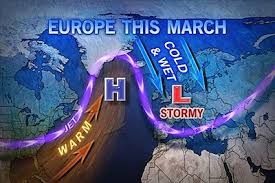
This winter’s weather has been weird across much of the Northern Hemisphere. Record storms in Europe; record drought in California; record heat in parts of the Arctic, including Alaska and parts of Scandinavia; but record freezes too, as polar air blew south over Canada and the U.S., causing near-record ice cover on the Great Lakes, sending the mercury as low as minus 50 degrees Celsius in Minnesota, and bringing sharp chills to Texas. Everyone is blaming the jet stream, which drives most weather in mid-latitudes. That would be a significant development.
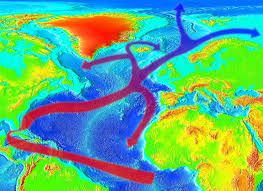
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center The polar jet stream may be driving a "hemispheric pattern of severe weather." For what happens to the jet stream in the coming decades looks likely to be the key link between the abstractions of climate change and real weather we all experience. So, is our recent strange weather a sign of things to come? Are we, "sleepwalking to a climate crisis"? The story gets tangled because trying to identify long-term trends amid the noise of daily weather is hard. The U.K. Met Office, which keeps a global weather watch, said in a rush report put out in mid-February that we are experiencing a "hemispheric pattern of severe weather," and that the events are linked. The most extreme days of the U.S. cold event, for instance, coincided with some of the most intense storms over the U.K. and physically the connection is through the polar jet stream, which the report said showed a "persistent pattern of perturbations" — in other words, it ran wild.
The polar jet stream is a narrow stream of fast wind circling the globe from west to east at the top of the troposphere from 7 to 12 kilometers up, and usually between 50 and 70 degrees north. It forms where cold, dense air from the Arctic meets warmer and less dense air from mid-latitudes. At the boundary, winds rush in to equalize the pressure difference. The earth's rotation diverts these winds to travel eastward. Climatologist Jennifer Francis links 'this bizarre winter' to changes in the jet stream caused by a warming Arctic As the jet roars around the world, it drags weather systems with it. Most of Europe's weather rides in under the jet stream from the Atlantic, and most of the western U.S.'s weather comes from the Pacific in a similar manner. This year, the jet has been unusually far north in the Pacific, bringing balmy weather to Alaska. But across the Atlantic it has been unusually far south, unusually persistent, and 30 percent faster than normal. It has sent more than 30 storms, many of them much larger and more intense than normal, crashing into the shores of Ireland and Britain in the past three months.
The largest Hurricane in living memory struck, the Dingle Peninsula and South west Ireland in early 2014 causing devastation and flooding. Homes were without telephone and power for many weeks, water was cut off as the pumping stations failed, will this become the norm?, asks Paul.
With the storms have come high winds and heavy rains almost every day, delivering amounts of precipitation unseen in records going back more than a century — and probably exceeding anything else in the last 250 years, according to the Met Office report. At the annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in Chicago this month, climatologist Jennifer Francis of Rutgers University linked "this bizarre winter" to climate change, and in particular to changes in the jet stream caused by a warming Arctic. "Weather patterns are changing," she said. "We can expect more of the same." Francis notes that the Arctic has been warming faster than the rest of the planet in recent decades, driven by melting ice that replaced reflective white surfaces with dark, energy-absorbing ocean. That is expected to continue. While lower latitudes will also warm, the result will be to reduce the temperature gradient between polar and mid-latitude air that drives the jet.
So, says Francis, we can expect the jet to slow.
 A slower jet is generally more meandering and inclined to get "stuck," delivering unchanging weather. There is one problem with this analysis as regards recent events, says Tim Woollings, who researches atmospheric dynamics at Oxford University in England. While the jet stream has indeed been "stuck" for the past two months, delivering cold weather to North America and storms across the Atlantic, it is not slow and meandering. Across the Atlantic at least, it has been fast and remarkably straight. "That is the exact opposite to the weak meandering jet of your hypothesis," Woollings told Francis in an email exchange last week that both shared with Yale Environment 360.
A slower jet is generally more meandering and inclined to get "stuck," delivering unchanging weather. There is one problem with this analysis as regards recent events, says Tim Woollings, who researches atmospheric dynamics at Oxford University in England. While the jet stream has indeed been "stuck" for the past two months, delivering cold weather to North America and storms across the Atlantic, it is not slow and meandering. Across the Atlantic at least, it has been fast and remarkably straight. "That is the exact opposite to the weak meandering jet of your hypothesis," Woollings told Francis in an email exchange last week that both shared with Yale Environment 360.That certainly doesn’t prove Francis wrong. Woollings agrees that Francis’s prediction of a stuck meandering jet looks very like the situation in the Pacific this winter. But it does complicate claims that this winter’s extremes can be blamed on man-made climate change Britain’s Met Office says the real driver of recent climate patterns has been the jet stream over the Pacific Ocean. So what is going on? The Met Office came to the conclusion that the real driver of the action in recent months was not in the Arctic or the Atlantic, but far away in the western Pacific Ocean.
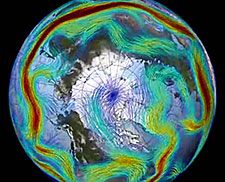
The jet stream, remember, is a global wind, circling the earth. This winter, the jet stream over the Pacific has been deflected much further north than usual. This, according to the Met Office, is likely a consequence of some combination of heavy rains over Indonesia, warm Pacific waters, and unusual pressure systems. The displaced Pacific leg of the jet stream dragged warm air up over Alaska. But, once east of the Rockies, it met the dense cold air of the Arctic and plunged south. A long way south — as far as Texas at times. This southward excursion of the jet brought freezing weather across much of the U.S. But it also brought that cold polar air into contact with warm southerly breezes. Thus the temperature gradient at the boundary between polar and non-polar air was exceptionally great.
At times, says Francis, Arctic air was meeting tropical air as the polar jet coalesced with the sub-tropical jet, which forms where tropical air meets air from the north. The scientists agree that this exceptional temperature difference dramatically speeded up the jet stream as it pushed out over the Atlantic on its unusually southerly trajectory. A fast jet stream is usually also a straight jet stream. And the southerly route allowed the surface air it pulled along to pick up unusual amounts of moisture evaporating from the warm waters of the Atlantic. The result was that the jet slammed a long succession of intense storms into southern England, where they would normally hit Scotland or miss the U.K. altogether. The storms contained huge volumes of moisture. And, to add to the tumult, the fast winds across the Atlantic also whipped up big waves and tidal surges; so in places record flood flows coming down rivers met flood waters coming off the sea. Parts of Britain were submerged. Where does this leave us on climate change? It is no great surprise that there is confusion. Weather is weather. It is always changeable, with a large Scientists remain uncertain about how the major features of world’s weather will respond to global warming. random element. Stuff happens.
The Met Office notes that the winter’s weird weather has a range of causes besides the jet stream, including unusual upper atmosphere winds over the North Pole, and anomalies in the eastern Pacific that have delivered severe drought to California. There is, the Met Office says, no compelling evidence from this winter to suggest that there is a new emerging pattern. But that doesn’t mean nothing is going on. Long-term trends are hard to spot, and natural variability is still generally dominant over the subtle changes in climate, or "average weather." Yet there are some instances where attribution is possible. For example, climate researchers have persuasively argued that a few intense heat waves — such as the one that killed 70,000 people in western Europe in 2003 — would have been highly unlikely without the added impetus of global warming. But for weather extremes other than rising temperatures, unambiguous attribution of even extreme events is very hard to make, whatever the suspicions that something is up.
Climate scientists remain very uncertain about how most of the major features of the world’s weather will respond to global warming. The climate will change, for sure, but exactly how is a tough call. El Niño, the Asian and African monsoons, Atlantic hurricanes, the jet streams: The most recent report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), issued last October, puts a big question mark over the likely trends for all of them. And while Francis suggests the polar jet stream should slow as the Arctic warms, the IPCC noted that most climate models predict a faster polar jet. Actual trends so far don’t tell us much.
According to the Met Office, the number of storms crossing the Atlantic in a normal year is no higher today than 150 years ago. But Xiaolan Wang of Environment Canada, a government agency, last yearreported evidence that winter storms are becoming stronger over the North Atlantic. This may not have anything to do with the jet stream, however. These storms could just be picking up more moisture from an Atlantic that is now substantially warmer than in past decades. Data from weather stations around the world reveal more extreme precipitation events — and more droughts, too. This is firmly in line with the predictions of climate models and is "what is expected from fundamental physics," says the Met Office.
A warmer atmosphere will contain more energy, and more moisture from evaporation, says Woollings. It already does. And, in general, more energy and moisture will mean wetter storms in many places.
Weird weather is definitely on the agenda, and the jet stream is very likely to be an important part of it. The nightmare scenario is that Francis will be proved right about the jet stream becoming more "stuck" in a particular trajectory, but that, as happened this winter, it will get stuck while travelling at express speed and bringing strong winds and heavy rain with it. The Met Office says the Francis scenario "raises the possibility that disruption of our usual weather patterns may be how climate change may manifest itself." If so, that would indeed unleash the perfect storm.

